Introduction
Nowadays, speaking English is the most important skill to be acquired by students for three basic reasons: first, it allows people to communicate around the world with just one language. Second, English has become the most common language used in magazines, books, newspapers, electronic devices, guides, and all mass media and of course the internet. This means that citizens of this world need to communicate in English. (Clavijo, 2016, p.22). Finally, speaking English is very important because it occurs in everyday life. Human beings use spoken language in every single situation of their lives. People are talking wherever they go, and to have skills in any spoken language helps in face to face conversation, to know what to say, where to say, and when to say something (Gudu, 2015, p. 55).
Gómez & Rodriguez (2008) stated that “The speaking skill is the ability to communicate our thoughts, feelings, needs and ideas by means of oral or verbal expressions” (p. 16). It is a productive skill which is difficult for some people and students to acquire because it involves more than just saying words. The speaker has to pronounce the distinctive sounds of a language, stress and rhythmic patterns, and intonation patterns of the language clearly enough so that people can understand what they say.
National Curriculum Guidelines EFL in Ecuador states that, the speaking proficiency of students at third year of Bachillerato, should have three important outcomes: a) to be able to sustain a direct description of a subject; b) to exchange, change and confirm information to solve problems and, finally c) to go into improvised conversations about familiar topics (Ministerio de Educación, 2014, p.25).
After a diagnostic test carried out by the teacher of the third grade of Bachillerato “E” at Unidad Educativa Chordeleg, it was detected a lack of proficiency in speaking skill in comparison with reading, listening and writing skills. Taking into account that teachers should keep in mind the fact that in a classroom there are students with different abilities, expectations, motivation, knowledge, and learning styles, a new strategy, Integrated- Tasks was proposed in order to overcome the problem. For Sotamba (2013) “the teachers should vary their approaches and offer as many opportunities as possible to make the whole class find a little something to hold on to, so as to expand and grow the development of the speaking skills” (p. 25).
Methodology
This study was focused in quasi experimental research that measured the effects of the use of Integrated- Tasks through Task-based instruction in enhancing speaking skills by quantification of the data through scores and ratings. In addition, a quantitative method was used to interpret, extend and explain data results to facilitate the readers understanding as well as a detailed description of the questionnaire applied to students to know the advantages and disadvantages of Integrated Task. The target population were 14 students of third grade Bachillerato, at Educational Unit Chordeleg during 2017 school year, 11 female and 3 male students with ages between seventeen to eighteen years old, who were chosen after getting the lower results of a diagnostic test.
A pretest was taken to know the English proficiency before the application of the treatment. The pretest was validated for the investigation department of Education Academic Unit through the operationalization of variables involved in this research.
The pretest was divided into four parts, one for skill, in the following way: listening skill had an audio called Breakfast with 01:44 minutes length, a handout with five multiple choice questions were handed to the students to be completed. Then, a reading The food guide Pyramid was given to the students which had ten true/false questions. The writing skill was performed by a comparative essay about health and junk food, 180 words as minimum. Finally, speaking skill was carried out to accomplish three parts: first, a description of a picture about food; second, answering structured questions about the picture presented which contains a family having dinner on Thanksgiving Day; and finally, they had a brief structured conversation about different topics to get to know more about student´s vocabulary, fluency and coherence. A rubric was used to grade the fluency and coherence of speaking.
The pretest was taken in two hour classes, the first one to evaluate the three skills listening, reading and writing, and the second hour was just for doing the speaking skill which is the aim of this investigation.
Integrated tasks through task-based instruction strategy to enhance the speaking skill was applied in six classes previously to conclude the first quimester of the school year 2017. The four skills were referred to as Receptive Skills (listening and reading) or Productive Skills (speaking and writing). Hence, integrating skills in the class were used by combining the receptive and productive skills, an example activity performed with the students to practice integrated skills is explaining as following:
Each class was performed in two hours. During the first hour the topics were explained following the teacher and students’ interaction through different activities like: brainstorming, free conversation, slide presentation, reading, writing documents, listening to records etc. The second hour was for performing the speaking activity only.
The topics for the classes, Having breakfast, Fruits, Food and drink, Food and nutrition, Recipes, and finally, Junk food were performed through different activities described above in the application of the pretest.
At the end of the treatment period a post test was taken, which was the same as the pretest, and it was applied to know the effect of the IT in improving speaking skill. A questionnaire about the advantages and disadvantages of the application of the Integrated-Tasks was applied to students at the end of the treatment period. In the first question, students were asked to rate the value of the IT used during the treatment period. The second question asked if the activities in the treatment period were interesting. The third question was about if the use of IT is a good method to improve speaking skill. The fourth question asked the students to put a check in the activities that they would consider the best ones to improve speaking skill. The fifth question asked if they had improved their speaking skill during the treatment period. Finally, the sixth question was about how they evaluate their speaking skill now compared to before.
Results
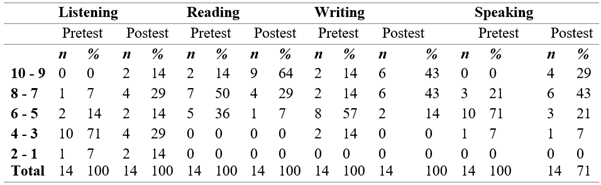
The application of the IT to enhance speaking skill was carried out with a pretest to show the starting point of the treatment period. After concluding the period of application of the methodology (six classes, two hours each one), a posttest was given to students to learn how much they had improved in their speaking skills. It is possible to see the results obtained in Table 1.
As it is shown in the table 1, in the listening skill students had an improvement in posttest of 14% in the high rank 10-9 and 29% in the rank of 8-7 being also noted the decreasing of low score in the rank of 4-3 which was high in the pretest.
The reading skill pre-test shows the students had already performed scores up to 50%, hence, it is remarkable that 64% of the students reached the higher score in posttest.
The writing skill pre-test shows that only 28% of the students reached the high ranks however, it shows a rise in the high scores in posttest reaching 43% in up to 8 ranks.
Finally, the speaking skill in the pre-test the majority of the students reached scores up to 50%and in the posttest they get 43% and 29% in the high scores.
At the end of the treatment period, a questionnaire was applied (Annex 3) to the students in order to know the advantages and disadvantages of the Integrated- tasks in the classroom. The results obtained were the following:
All of the students considered very important the Integrated- tasks because the classes were very active and fun, consequently the students found interesting all the activities performed in class.
The students agreed that the use of the IT is a good method to improve speaking in English. The activities that they found the best ones to improve speaking skills were: listening, reading, and writing because the three skills joined together made understandable the class and helped them to develop English as a whole. Four students mentioned that listening is the most important activity because every language starts learning by hearing. Two of them said that reading is the most important activity because it makes the writing easier and words are much more comprehensible. Finally, two students remarked that writing should be learned first followed by listening and reading.
About improving the speaking skill during the treatment period, except one of them mentioned that they have improved their speaking skill noticing that is better now than before because their pronunciation and vocabulary has improved. However, one student reported that his speaking had not been improved due to the lack of responsibility.
Motivation focused on the variety of activities performed in class were the key to improve the environment where students felt confidence enough to improve the speaking skill. Consequently, active classrooms with updated methodologies or a combination of different ones help to keep the interest in the topic of the class.
Discussion
The results of this study agree with Gómez & Rodriguez, (2008) who state “the use of IT is a very useful strategy which will allow us to use a variety of activities during the instruction in order to improve the students’ speaking skill” (p.58). Therefore, students had the opportunity to interchange their thoughts and doubts about the topic which involved vocabulary, grammar, structure, pronunciation, and comprehension.
The data of these investigation also show the concordance with Halici & Mede´s work (2018) who states that the task-based approach activities are really useful in the classroom because they inspire teachers teaching speaking through oral activities that students consider and find interesting, funny and different, this makes easier the language acquisition in speaking skill and even in the other skills. This gives teachers the chance to innovate their classes for students, who will enjoy speaking and will apply the language naturally and, consequently, the students will be able to use the language not only in class, but they will use the language daily as a tool of real communication.
Also, an investigation study made by (Orellana Mora, 2011, p. 80) shows how the application of task-based instruction in second language learners which is based in different kinds of activities in the class, made students enhance their English language knowledge not only in speaking skill, but in other skills as well.
In this way, the results found that students increased their level in listening and reading skills more than in writing and speaking skills. This is relevant because it means for sure that the use of this strategy helped them be better in the four basic skills. Nevertheless, reading skill was mostly increased, that this study reflects students got a better level in reading skill, more than in speaking skill which was expected.
Another important fact is the use of CBI, which in the same way as task based instruction, allows teachers to utilize different kinds of materials to teach the topic of each class giving the priority to and setting the knowledge students consider relevant (Cenoz, 2015, p. 10-11).
The results are similar shown in an investigation made by Amiri & Hosseini (2014). The students demonstrated that the use of CBI as strategy of learning developed their English knowledge in the four basic skills. The results of this study agree with the fact that students do improve their English knowledge with the use of CBI, primarily based in the topic of the class. This should be addressed by student’s social environment interest. For these reasons, it is important to mention that the IT does really increase the student’s English knowledge through the Task- based instruction and the Content- based instruction, which become relevant tools in the teaching and learning process (p.2159-2162).
The strategy in question involves four skills: listening, speaking, reading and writing in order to improve students´ interactions with each other and the teacher resulting in an improved speaking outcome.
The use of integrated task [IT] finds its foundation in the Vygotsky’s theory, which maintains that social interaction precedes development. According to this author, humans use tools to communicate their needs. He believed that internalization of these tools leads to higher thinking skills. Consequently, social interaction plays a fundamental role in the development of cognition. Vygotsky also states that cognitive development is the result of a dialectical process, where the child learns by sharing experiences and solving problems with someone else, such as parents, teachers, siblings, or a more competent peer (Feryok, 2017, p.717).
This theory helps the teachers to encourage the students to work and share their ideas, feelings, and opinions with their partners in order to learn from those who have a higher level of knowledge and language proficiency.
Typically, many schools have traditionally held a model in which a teacher or lecturer “transmits” information to the students. In contrast, Vygotsky’s theory promotes learning contexts in which students play an active role in learning. The roles of the teacher and student are therefore shifted to where the teacher collaborates to help and facilitate meaningful construction in students. Learning becomes a reciprocal experience for students and teachers. (Gómez & Rodriguez, 2008, p. 14)
To sum up, Vygotsky’s theory mentions that children learn better by interacting with others and the key of effective learning lies in the nature of the social interaction between two or more people with different levels of knowledge. Vygotsky theory is very useful for teaching through IT because of the interaction between students in order to perform their activities.
According to Gómez & Rodriguez (2008), “Integrated Tasks are activities that link the different language skills such as writing, reading, listening, speaking, grammar, vocabulary, spelling, pronunciation, and other factors such as the characteristics of the teacher, the learner, the setting, and the relevant languages during the instruction” (p. 25). Integrated- Tasks allow teachers and students to acquire a great amount of knowledge in a language through speaking in class. It is considered a good method to learn a second language in an easy way (Morton, 2016). Different activities that teachers use with IT method are: reading comprehension, description, role plays, presentations, listening to records, audios, songs, filling in blanks, brain storming, essays, interviews, etc, for integrating and improving speaking skill (Gómez & Rodriguez, 2008).
The two basic ways to use IT in the classroom are: a) content based language instruction and b) task-based instruction. Both are strategies that benefit students and teachers by using a variety of materials, textbooks, and technologies, which help to enhance language acquisition and have had good outcomes in the classrooms.
Content based instruction is defined by Richard and Rodgers (2001) as “[…] teaching of content or information in the language being learned with little or no direct or explicit effort to teach the language itself separately from content being taught” (p.204), that is why this approach is considered as a realistic method of teaching because it combines language and content learning.
Stryker and Leaver (2007) consider that CBI encourages students to learn a new language from the beginning by communication of real situations, providing tools to the students to be autonomous According to these authors, the experience in Foreign Language classrooms has demonstrated how students have accelerated the process of acquisition of a language through cross-cultural knowledge, thus making their learning experience more enjoyable.
According to the Li (2016) “the task- based instruction is different from other more traditional methods of language teaching. Lessons are constructed according to the language required to perform specific tasks rather than according to the aspects of language such as structure and vocabulary”. (p.73) Consequently, students participate in pair and group work activities that require comprehending, producing, manipulating, or interacting with the target language; paying special attention to meaning rather than to form. Activities will help to increase student’s interaction and collaboration.
An important fact to be considered in Task-based instruction is that the nature of tasks can vary from one level to another, according to the students’ background. Therefore, tasks become increasingly complex at higher proficiency levels. Selection of a greater variety of materials to use in class, like textbooks, and technologies will promote the integration of the four skills. However, the main issue is that teachers should know that teaching language learning strategies and emphasis in a strategy can often enhance performance in multiple skills (Gómez & Rodriguez, 2008, p. 26).
A few investigations have been done about the use of Integrated-task in our country. A research project, carried out in Guayaquil, using English teaching based in different activities for speaking and listening skills in English for Specific Purposes (ESP) for students of medicine shows how through activities such as: recorded audio journals, conversation tables, on-line practice activities, presentations based on medical readings and role-play conversations, resulted that conversation tables and training in formal presentations on medical topics were the most successful learning activities to improve speaking skills (Romero, 2017).
Another research in Cuenca used Task- based activities to foster the speaking skills in students of secondary school. Teenagers definitely enhanced their speaking skill through activities such as role play, reading comprehension, dialogues, putting images in order, etc., that encourage them to participate in a communicative way with the help and guide of their teacher and the collaborative work (Bermeo, 2013, p. 85).
Conclusions
In conclusion, this investigation demonstrated that:
The benefits of the use of IT to enhance the speaking skill in third grade of Bachillerato at Unidad Educativa Chordeleg, were first of all an improvement of speaking skill targeted by a variety of activities done during the treatment period. In addition, the benefits were extended to enhancing, besides speaking, the other skills like listening, reading and writing.
To evaluate the application of the Integrated- tasks in enhancing the speaking skill, the questionnaire applied to the students demonstrated that the students considered very important the Integrated- tasks, as well as the activities performed during the treatment period.
Thus, they think that their speaking skill was improved due to listening, reading, and writing joined together making the classes understandable and helping them to develop English as a whole.