I. INTRODUCTION
THE fall armyworm,Spodoptera frugiperda, is a significant insect pest of various important agricultural crops(1). It is native to subtropical and tropical areas of America(2).S. frugiperdawas discovered in western Africa in January 2016(3),(4)and in India in May 2018(5). In Pakistan, the presence ofS. frugiperdaon maize crop was reported in 2019(6).
More than 350 species of plants have been identified which are the hosts ofS. frugiperda(7). Other than maize, this pest has a wide host range, particularly soybeans, rice, cotton, and sorghum(7),(8). The larvae ofS. frugiperdahave the potential to damage more plant species, leading to significant reductions in yields of economically important crops(8). Several studies have confirmed the susceptibility of this pest to various economic crops(7),(10). Without any control measures, the annual maize losses in Africa have been reported to be 8.3 million to 20.6 million tons. These losses might reach 2531 million to 6312 million USD annually(11).
The nutritional value of the host plant affects the population growth of any insects(12). The nutrition that insects consume from their host plants significantly impacts their growth, reproduction, and survival(13). In order to investigate how different insect pests impact various plants through their feeding behavior, it is imperative to conduct fundamental biological research on the feeding habits and consumption patterns across different host plants.S. frugiperda, while having a preference for maize as its primary crop, can also target alternative crops in the absence of maize availability(14). There is a need to investigate howS. frugiperdaaffects economically important crops such as rice, sorghum and wheat, given the continued spread of pests in Pakistan.
Wheat (Triticum aestivum) holds paramount global importance as a widely cultivated crop. It stands as a staple food crop in Pakistan and plays an important role in the economy of our country. Wheat contributes 9.6 % of the agricultural sectors output and 1.9 % of the nations GDP, which highlights the significance of improving wheat production(15). According to earlier research done in Brazil, femaleS. frugiperdapreferably lays eggs on the upper part of the wheat crop rather than on other parts of the plant(16). TheS. frugiperdacan harm wheat crops at any phase of growth, from the booting to the milking period. A large population ofS. frugiperdalarvae may accelerate the maturation of wheat in areas where the pest migrates throughout the year(17),(18).
The pest status ofS. frugiperdais predominantly determined by the growth stages of the host plant infested(19). Consequently, to effectively evaluate the potential harm inflicted byS. frugiperdais essential to examine the influence of different wheat varieties on the pests growth. Understanding this relationship is crucial to accurately assess the risk of damage thatS. frugiperdaposes to wheat crops, as well as to develop an overall understanding of its potential impact. There is limited research available on the influence of wheat compared to maize on the consumption and rate of development ofS. frugiperda. Also, is becoming a significant pest to other crops such as cotton and soybeans in different countries(19). We hypothesize thatS. frugiperdawill inflict damage on wheat varieties. In addition, we expect to observe significant differences in the nutritional physiology of the insects when feeding on different wheat varieties compared to maize, indicating potential impacts on their development and survival rates.
II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
A. Collection and rearing of Spodoptera frugiperda
Spodoptera frugiperdaegg batches and larvae were collected from a maize field near University of Sargodha. The eggs were placed in petri dishes, and the neonate larvae were provided with a natural diet (maize leaves). Fresh maize leaves were used as the primary food source and the larval diet was replaced every 24 hours until they reached the pupal stage. Upon pupation, the pupae were separated and placed in plastic cages until the emergence of adults. The adult moths were paired and kept in rearing cages to facilitate oviposition. The larvae from F3 generations were used for further study.
B. Host plants
The seeds of five varieties of wheat (Dilkash-20, Fakhar-E-Bhakkar-17, Subhani-21, Faisalabad-08, and Akbar-19), and one variety of maize (NK-6654) were purchased from the local market of Sargodha. The wheat varieties were selected based on their extensive cultivation by farmers in the selected region. The seeds were set in plastic pots measuring 11x12 cm. Throughout the study, the proper agronomic practices were followed including irrigation and removal of weeds.
C. Nutritional physiology of Spodoptera frugiperda on different hosts
The second instar larvae were obtained from a reared culture. Prior to their release into the experimental arena (petri plates), the larvae were subjected to 24 24-hour period of starvation. Each petri plate contained one larva and was considered as one replication. Almost the same size and weight of leaves from each tested hosts were provided to each larva on a daily basis. The treatments were replicated three times and 10 larvae were tested in each replication. The weighted amount of leaves from each host was provided to larvae and replaced after 24 hours. The experiment was conducted under controlled laboratory conditions (25 ± 2 °C temperature, 70 ± 10 % RH, and a photoperiod of 14h10 from Monday to Sunday). The data of the developmental period of each larval instar, pupal stage, and adult stage was recorded on a daily basis. The length of the larvae was measured before and after a 24 hour feeding period using a measuring scale. Furthermore, the weight of each larva and its feces was measured on a daily basis using a digital weight balance. Similarly, the weight of the diet provided to the larvae was measured before and after the 24 hour feeding period to determine the consumption rate. Larval mortality data was also recorded daily throughout the duration of the experiment. The parameters of the feeding rates that were calculated from the recorded data (shown in Table 1) were based on Waldbauer’s formulas (20).
III. RESULTS
A significant difference was recorded in the relative consumption rate (RCR) ofS. frugiperdaamong different host plants at 1 day (F = 1381.0, P < 0.001), 3 days (F = 1374.0, P < 0.001), 5 days (F = 814.0, P < 0.001) and 7 days (F = 1205.0, P < 0.001) of feeding. Results revealed that the RCR value ofS. frugiperdawas higher when the larvae fed on maize (5.16- 8.08 g/g/day), followed by Fakhar-E-Bhakkar-17 (3.99- 7.00 g/g/day), and Akbar-19 (3.13 to 6.06 g/g/day). The lowest RCR value ofS. frugiperdawas recorded on Dilkash-20 (0.98-2.98 g/g/day) and Subhani-21 (1.47-4.05 g/g/day) by 1 week of feeding (Table 2).
A significant difference was recorded in the relative growth rate (RGR) ofS. frugiperdaamong different host plants at 1 day (F =1167, P < 0.001), 3 days (F=746.0, P < 0.001), 5 days (F = 679.0, P < 0.001) and 7 days (F = 229.0, P < 0.001) of feeding. The RGR ofS. frugiperdalarvae was higher on maize (1.20 to1.50 g/g/day), followed by Fakhar-E-Bhakkar-17 (0.89 to 1.24g/g/day) in 1 week of feeding. When larvae fed on Akbar-19, the relative growth rate was 0.62-1.04 g/g/day. The lowest RGR value ofS. frugiperdalarvae was recorded on Dilkash-20 ranging from 0.10-0.38 g/g/day in 7 days (Table 3).
A significant difference was recorded in the relative efficiency of conversion of ingested food (ECI) ofS. frugiperdaamong different host plants at 1 day (F = 5322.0, P < 0.001), 3 days (F = 2460.0, P < 0.001), 5 days (F = 2822.0, P < 0.001) and 7 days (F = 1924.0, P < 0.001) of feeding. Results showed that the ECI percentage ofS. frugiperdawas significantly higher on maize (17.92 to 25.09 %) for 1 week of larvae feeding as compared to other wheat varieties. However, the ECI percentage was 15.6-21.4% on Fakhar-e-Bhakkar-17 and 13.7-19.7% on the Akbar-19 variety of wheat. The lowest percentage of ECI was 4.05 to 7.937 % on Dilkash-20 (Table 4).
IV. DISCUSSION
Spodoptera frugiperdais a polyphagous pest that feeds on a wide range of crops(9). Damage caused by this pest can lead to significant yield losses in wheat production, so one aspect of the research focuses on the evaluation of nutritional indices of S. frugiperdain various wheat varieties, with the objective of designing pest management strategies. Although maize is the preferred host forSpodoptera frugiperda, the feeding parameters of this pest on Fakhr-e-Bhakkar-17 and Akbar-19 wheat varieties were almost similar to those observed on maize. The relative consumption and growth rate of the pests, as well as the conversion efficiency of the ingested feed, were satisfactory in these two wheat varieties. These findings regardingS. frugiperdafeeding on wheat plants are in agreement with the results of Zhang et al.(17).
According to Gebretsadik et al(21), the development ofS. frugiperda, including the duration of larval and pupal stages, adult longevity and survival, was significantly influenced by maize compared to other crops. Our results showed that the feeding indices parameters, including relative consumption and growth rate and ingested feed conversion efficiency, were satisfactory when the larvae fed on wheat varieties Fakhr-e-Bhakkar-17 and Akbar-19, compared to maize. These results suggested that these varieties may be susceptible toS. frugiperdainfestation. It should also be mentioned that other factors, such as plant age and abiotic stress, may also affect the nutritional quality of wheat and consequently influenceS. frugiperdafeeding and growth. Feed conversion efficiencies of S. frugiperdalarvae show significant variations in different host plants. This phenomenon is not unique to this pest, but is a general characteristic observed in almost all insects. A potential factor contributing to this variability could be the ability of insects to make homeostatic adjustments in their consumption rates and efficiency parameters.
These adjustments allow insects to achieve their ‘ideal’ growth rate, even when consuming foods of varying quality(22).
Even though the main host of fall armyworm remains corn, the results of the study suggest that it can also feed on wheat. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor fall armyworm infestation in wheat crops and employ integrated pest management techniques to effectively control the pest population. The nutritive quality of a host plant can significantly impact on feeding and growth of herbivorous insects includingSpodopterasp(23). Several researchers have examined the effect of host plants on the nutritional indices of insect pests(22),(24). Awmack & Leather(13)reported that the nutritional value and quality of host plants are crucial.
Table II Relative Consumption Rate (Means±SE) of Spodoptera Frugiperda Feeding on Different Wheat Varieties in Comparison to Maize
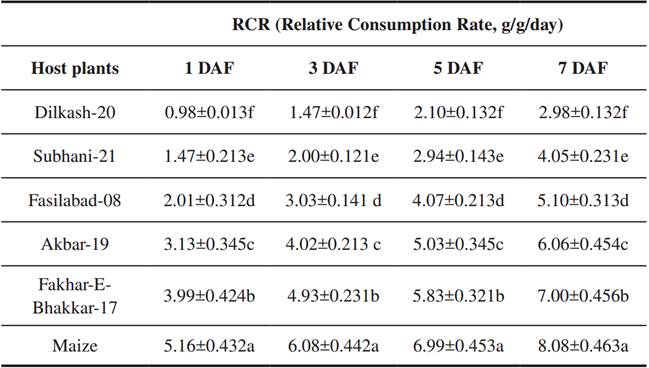
DAF = days after feeding, Means sharing similar letters within a column are not significantly different at p=0.05.
Table III Relative Growth Rate (Means±SE) of Spodoptera Frugiperda Feeding on Different Wheat Varieties in Comparison to Maize
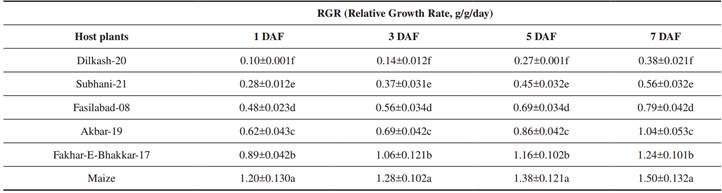
DAF = days after feeding, Means sharing similar letters within a column are not significantly different at p=0.05.
Table IV Relative Efficiency of Conversion of Ingested Food (Means±SE) of Spodoptera Frugiperda Feeding on Different Wheat Varieties in Comparison to Maize
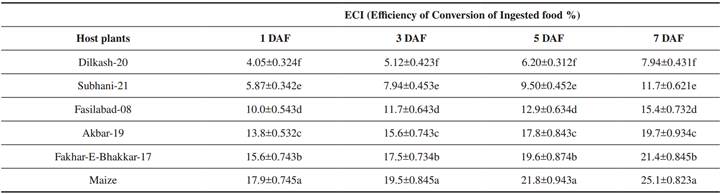
DAF = days after feeding. Means sharing similar letters within a column are not significantly different at p=0.05.
Factors within the plant characteristics that impact insect survival and fitness. Insects are highly dependent on their diet for development(25), and the utilization of various plant food sources introduces variation in insect vita variables(8),(26). Our study demonstrated thatS. frugiperdahad higher relative growth rates, consumption rates, and conversion efficiency of ingested food in maize and two wheat varieties Fakhar-E-Bhakkar-17 and Akbar-19. These results suggest that the nutritional quality of a host plant can have a significant impact on the feeding and growth of insect herbivores. This preference could be attributed to the nutrition of these plants, which could be preferable for the insect(19).
Insects are known to improve their ability under optimal larval feeding conditions, as shown by studies such as those of Barros et al.(19)and Xu et al.(27). Evaluating the adequacy of particular food sources for insect development may involve consideration of several indicators of suitability. Each plant species possesses a number of secondary metabolic and nutritional compounds, each with distinct defensive attributes, encompassing tolerance, antibiosis, antixenosis, and various combinations of these three mechanisms(28).
The results of this study will contribute to the understanding of the biology ofS. frugiperda, which could help in its management and control. Consequently, future research is needed on the examination of a wider range of host plant species conducive to the development ofS. frugiperda. In addition, evaluation of the chemical constituents of these host plant species would improve understanding the mechanisms underlying host suitability.
The cropping system, particularly the practice of intercropping, is explored as an alternative approach to the management arthropod pests affecting crops, as discussed by Smith and McSorley(29). However, in our country, farmers grow maize and wheat crops at the same time. Some crops are known to exert a deterrent influence on herbivores.
This is attributed to the potential alteration of the ability of pests to locate their host plants through visual and smell interference caused by cultivated vegetation(30). Conversely, certain crops can create a favorable microenvironment for insects(31),(32). Our study was conducted under controlled conditions and the results showed thatS. frugiperdacan successfully feed on two wheat varieties.
However, the potential of wheat crops with a maize cropping system warrants further investigation to test the incidence ofS. frugiperdaon wheat crops under field conditions. In addition, this study did not evaluate the nutritional composition of different wheat varieties. Therefore, future research could attempt to quantify the precise nutritional content and assess quality variations among host plant conditions. This would facilitate a more complete understanding of the influence of nutrition on ecological and physiological traits.
V. CONCLUSION
Our study revealed that the nutritional physiology of S. frugiperda was satisfactory on maize and some wheat varieties as well. The findings of the study have important implications for pest management strategies and crop breeding programs in wheat cultivation. Moreover, the presence of various crops within the agro-ecosystem, notably wheat and maize, can induce altered feeding preferences when the primary host is not available. The results of this research indicate that S. frugiperda could become a pest on other agricultural plants in the future, especially wheat. Future studies should prioritize the examination of a broader spectrum of host plants to assess nutritional indices relevant to S. frugiperda. Additionally, evaluating the chemical components of the tested cultivars would provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying host suitability.
No funding was available for this research work. The authors are thankful to the Department of Plant Pathology, University of Sargodha, for providing research facilities. All the authors contributed equally.